
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
2 Hong Kong Polytechnic University Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen 518000, China
3 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
4 Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
5 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
6 Photonics Research Institute, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
7 e-mail: chao.lu@polyu.edu.hk
8 e-mail: puxiang.lai@polyu.edu.hk
Multimode fibers (MMFs) are a promising solution for high-throughput signal transmission in the time domain. However, crosstalk among different optical modes within the MMF scrambles input information and creates seemingly random speckle patterns at the output. To characterize this process, a transmission matrix (TM) can be used to relate input and output fields. Recent innovations use TMs to manipulate the output field by shaping the input wavefront for exciting advances in deep-brain imaging, neuron stimulation, quantum networks, and analog operators. However, these approaches consider input/output segments as independent, limiting their use for separate signal processing, such as logic operations. Our proposed method, which makes input/output segments as interdependent, adjusts the phase of corresponding output fields using phase bias maps superimposed on input segments. Coherent superposition enables signal logic operations through a 15-m-long MMF. In experiments, a single optical logic gate containing three basic logic functions and cascading multiple logic gates to handle binary operands is demonstrated. Bitwise operations are performed for multi-bit logic operations, and multiple optical logic gates are reconstructed simultaneously in a single logic gate with polarization multiplexing. The proposed method may open new avenues for long-range logic signal processing and transmission via MMFs.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(3): 587
1 中国建筑材料科学研究总院有限公司, 北京 100024
2 中国长江三峡集团有限公司, 武汉 430010
低热硅酸盐水泥因水化热低而被大量应用于高等级大体积混凝土工程以降低温度应力给结构带来的开裂风险。此外, 高温下强度增长稳定的特点决定其能在高热施工环境发挥作用, 优良的体积稳定性有利于解决混凝土结构开裂问题, 较高的后期强度和优良的抗侵蚀性能适合用于高性能混凝土的制备。本文从水化、性能等角度出发, 分析了低热硅酸盐水泥在水化调控、水化产物及微观结构、性能优化等方面存在的部分问题, 总结了低热硅酸盐水泥高温耐受、抗侵蚀、体积稳定等性能特点, 提出了低热硅酸盐水泥在严酷环境、高热环境中的应用展望。
低热硅酸盐水泥 硅酸二钙 水化 耐久性 抗裂性能 low-heat Portland cement dicalcium silicate hydration durability crack resistance
1 钢铁研究总院, 北京 100081
2 阳江市五金刀剪产业技术研究院, 广东 阳江 529533
3 兰州理工大学, 甘肃 兰州 730050
在激光选区熔化技术中,激光-粉末的相互作用会对粉末特性产生重大影响,而在粉末循环使用过程中粉末特性的变化规律和演变机理尚不明确。本文利用激光粒度仪、扫描电子显微镜、能量色散型光谱仪研究了激光选区熔化粉末的粒径、物理特性、表面形貌、元素含量、微观组织在循环使用过程中的变化规律。研究结果表明:随着316L不锈钢粉末循环使用次数的增加,粉末的粒径分布、形貌、表面成分、表面微观组织和氧化程度都发生了较大变化;粉末的堆积特性如松装密度、振实密度、流动性也发生了不同程度的变化;另外,循环使用的粉末颗粒表面生成了富含硅、锰元素的圆形氧化斑点。本文将循环粉末中的异形颗粒分为两类——激光诱导熔池溅射颗粒和气体夹带诱导异形颗粒,并详细讨论了两类异形颗粒的形成机理。本文研究结果表明316L奥氏体不锈钢在循环使用过程中会产生弱磁性粉末颗粒。
激光技术 激光选区熔化 循环使用 氧化斑点 粉末特性 演变机理 中国激光
2021, 48(14): 1402009
1 中国海洋大学信息科学与工程学院海洋技术系, 山东 青岛 266100
2 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室区域海洋动力学与数值模拟功能实验室, 山东 青岛 266237
3 深圳市环境监测中心站, 广东 深圳 518049
4 深圳市国家气候观象台, 广东 深圳 518040
5 青岛镭测创芯科技有限公司, 山东 青岛 266101
相干多普勒激光雷达作为观测风场信息的有效探测工具,广泛应用于不同场景的风场以及大气观测。2019年8月,研究人员利用相干多普勒激光雷达在深圳市石岩综合气象观测基地连续开展了13 d的风廓线观测实验。分析了多普勒波束扫描模式下五波束法、三波束法和二波束法反演结果的异同及这些方法对测风精度和数据获取率的影响。数据比对结果表明,三波束法和二波束法的反演结果与五波束法所得结果有较好的一致性。针对激光雷达实际观测中系统或大气状态如云雾、降水等导致个别波束信噪比较低的问题,需灵活选取波束以反演风场、增加数据获取率,得到的探测高度平均提高量为100~400 m。
大气光学 激光雷达 多普勒波束扫描模式 精度 获取率 光学学报
2021, 41(10): 1001001
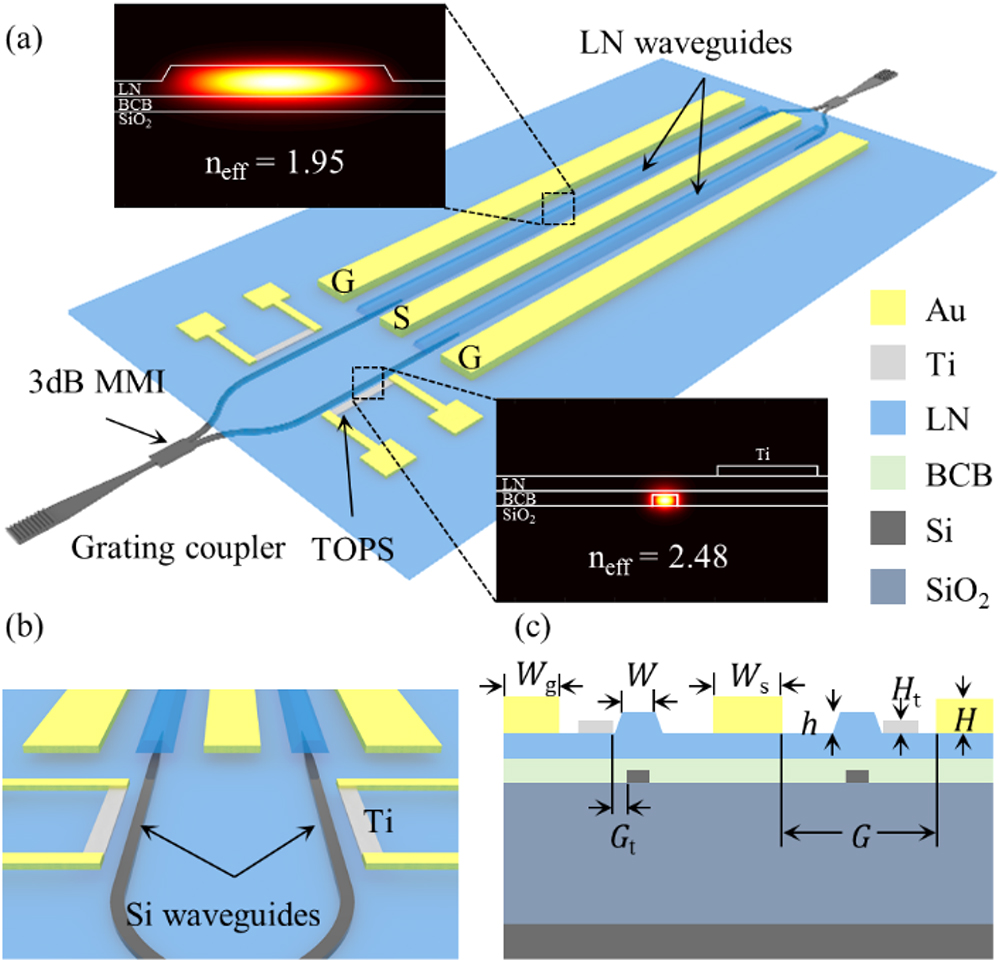
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies and School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510000, China
2 Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Information Materials and Technology, South China Academy of Advanced Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Higher-Education Mega-Center, Guangzhou, China
3 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, Photonics Research Centre, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China
4 State Key Laboratory for Modern Optical Instrumentation, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Sensing Technologies, Zijingang Campus, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
Optical modulators have been and will continue to be essential devices for energy- and cost-efficient optical communication networks. Heterogeneous silicon and lithium niobate modulators have demonstrated promising performances of low optical loss, low drive voltage, and large modulation bandwidth. However, DC bias drift is a major drawback of optical modulators using lithium niobate as the active electro-optic material. Here, we demonstrate high-speed and bias-drift-free Mach–Zehnder modulators based on the heterogeneous silicon and lithium niobate platform. The devices combine stable thermo-optic DC biases in silicon and ultra-fast electro-optic modulation in lithium niobate, and exhibit a low insertion loss of 1.8 dB, a low half-wave voltage of 3 V, an electro-optic modulation bandwidth of at least 70 GHz, and modulation data rates up to 128 Gb/s.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(12): 12001958

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Photonics Research Centre, Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Kowloon, Hong Kong
2 National Engineering Laboratory of Next Generation Internet Access Networks, School of Optical and Electronic Infor-mation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Multicore fiber (MCF) which contains more than one core in a single fiber cladding has attracted ever increasing attention for application in optical sensing systems owing to its unique capability of independent light transmission in multiple spatial channels. Different from the situation in standard single mode fiber (SMF), the fiber bending gives rise to tangential strain in off-center cores, and this unique feature has been employed for directional bending and shape sensing, where strain measurement is achieved by using either fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs), optical frequency-domain reflectometry (OFDR) or Brillouin distributed sensing technique. On the other hand, the parallel spatial cores enable space-division multiplexed (SDM) system configuration that allows for the multiplexing of multiple distributed sensing techniques. As a result, multi-parameter sensing or performance enhanced sensing can be achieved by using MCF. In this paper, we review the research progress in MCF based distributed fiber sensors. Brief introductions of MCF and the multiplexing/de-multiplexing methods are presented. The bending sensitivity of off-center cores is analyzed. Curvature and shape sensing, as well as various SDM distributed sensing using MCF are summarized, and the working principles of diverse MCF sensors are discussed. Finally, we present the challenges and prospects of MCF for distributed sensing applications.
optical fiber sensing distributed optical fiber sensing multicore fiber space-division multiplexing Opto-Electronic Advances
2020, 3(2): 02190024
1 兰州理工大学省部共建有色金属先进加工与再利用国家重点实验室, 甘肃 兰州 730050
2 钢铁研究总院, 北京 100081
3 阳江市五金刀剪产业技术研究院, 广东 阳江 529533
采用选区激光熔化(SLM)技术技术制备了成形良好的块状CoCrW合金,研究了热处理工艺对CoCrW合金相组成、组织及显微硬度的影响。通过JMATPro软件模拟计算了CoCrW合金的平衡相图;利用X射线衍射分析仪、扫描电子显微镜、显微硬度计对热处理前后合金的相组成、组织、显微硬度进行了测试。结果表明:SLM制备的原始试样主要由γ相以及少量ε相组成,热处理后大量的γ相转变为ε相,且有块状、条状析出相产生;在较低的热处理温度下,熔合线处析出相的尺寸较大,与其他部位的区别比较明显;随着热处理温度升高,晶粒长大,晶界处析出相(δ相)长大,且与熔合线处的差别减小;热处理后,CoCrW合金的显微硬度有所降低,其中1100 ℃水冷试样硬度的降幅最大。
激光技术 选区激光熔化 热处理 显微组织 显微硬度 中国激光
2019, 46(10): 1002002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
2 Photonics Research Centre, Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China
3 QXP Technology Inc., Xi’an 710119, China
4 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, XIOPM, CAS, Xi’an 710119, China
5 e-mail: zhe.kang@polyu.edu.hk
6 e-mail: saitchu@cityu.edu.hk
Passive all-optical signal processors that overcome the electronic bottleneck can potentially be the enabling components for the next-generation high-speed and lower power consumption systems. Here, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a CMOS-compatible waveguide and its application to the all-optical analog-to-digital converter (ADC) under the nonlinear spectral splitting and filtering scheme. As the key component of the proposed ADC, a 50 cm long high-index doped silica glass spiral waveguide is composed of a thin silicon-nanocrystal (Si-nc) layer embedded in the core center for enhanced nonlinearity. The device simultaneously possesses low loss (0.16 dB/cm at 1550 nm), large nonlinearity ( at 1550 nm), and negligible nonlinear absorption. A 2-bit ADC basic unit is achieved when pumped by the proposed waveguide structure at the telecom band and without any additional amplification. Simulation results that are consistent with the experimental ones are also demonstrated, which further confirm the feasibility of the proposed scheme for larger quantization resolution. This demonstrated approach enables a fully monolithic solution for all-optical ADC in the future, which can digitize broadband optical signals directly at low power consumption. This has great potential on the applications of high-speed optical communications, networks, and signal processing systems.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(10): 10001200
1 兰州理工大学 省部共建有色金属先进加工与再利用国家重点实验室, 甘肃 兰州 730050
2 阳江市五金刀剪产业技术研究院, 广东 阳江 529533
3 中国钢研科技集团有限公司, 北京 100081
采用选区激光熔化技术成形18Ni300马氏体时效钢, 并对成形件经固溶时效热处理研究。结果表明, 固液界面前沿的温度梯度与凝固速率的比值(G/Vs)决定了沉积态微熔池底部到顶部的胞-柱状枝晶的微观演变; 而在微结构区域存在的六角胞、伸长胞及条带组织的相互过渡是通过几何拓扑变换来实现。经热处理后, 沉积态胞状、柱状及亚微米组织结构消失, 出现细小板条状马氏体, 并在马氏体基中形成细小颗粒状沉淀相; 而热处理前后性能测试表明, 经固溶时效热处理后, 维氏显微硬度增加, 抗拉强度也显著增加, 延伸率降低, 断口形貌呈现典型的韧性断裂。
选区激光熔化 18Ni300马氏体时效钢 固溶时效热处理 组织 力学性能 selective laser melting 18Ni300 maraging steel solution and aging heat treatment microstructure mechanical properties
1 阳江市五金刀剪产业技术研究院, 广东 阳江 529533
2 阳江东华激光智能科技有限公司, 广东 阳江 529533
3 钢铁研究总院, 北京100081
4 阳江职业技术学院, 广东 阳江 529500
利用选区激光熔化技术制备GH4169试样, 采用光学显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、电子万能材料试验机分别分析了成型件的宏观及微观组织形貌和力学性能。结果表明, 选区激光熔化成型件的结晶形貌主要为胞状结晶形态, “微熔池”内部的细小的柱状晶直径约为0.1~1.0 μm, 截面成近似六角形的形状; 选区激光熔化过程中, 由于激光照射角度不同、铺粉不均匀、温度累积及散热条件的变化, “微熔池”内部细小柱状晶的形状、长度、宽度会有所差别; 选区激光熔化GH4169成型件拉伸试样呈现韧性断裂+解理断裂模式。
选区激光熔化 增材制造 组织分析 拉伸性能 selective laser melting additive manufacturing microstructure analysis tensile properties





